When Asteroid started, we built ReAct-style agents. These agents relied on a single, long prompt containing all the instructions. Equipped with browser tools, the agent would then try to complete the task in one go.
This approach was flexible—they could navigate sites, fill forms, extract data—but brittle. One long prompt meant limited control. How do you ensure the agent follows the right instruction at step 112?
When you’re automating insurance claims or updating patient records, “it usually works” isn’t good enough. One mistake can mean denied coverage, data loss, or compliance issues. So, we rebuilt Asteroid from the ground up—with graphs at the core.
💡 Too lazy to read? Try the new graph-based browser agent builder in Asteroid.
Why ReAct Agents Weren’t Reliable Enough
We ran into five core issues:
1. Context Overload
Browser agents consume huge context—DOM trees, screenshots, multi-step workflows. As the task grows, they lose focus. We saw agents fail more frequently in later steps, even if they started strong.
2. Black Box Execution
Failures were opaque. ReAct agents are essentially one big loop. When something went wrong, it was hard to tell why. Did it misunderstand the instruction? Click the wrong thing? With no clear state transitions, debugging was guesswork. What actions should we do to make the agent better?
3. All-or-Nothing Failures
A single mistake could derail an entire workflow. If step 8 of a 12-step process failed, the entire automation would collapse.
4. Too much Agency
Many workflows are partially deterministic. You don’t want the agent reasoning through everything. Sometimes it should follow a fixed path—e.g., script → agent → API → agent. ReAct made this clunky.
5. Vision or Non-Vision
Some sites work best with structured DOM interaction. Others require vision-based understanding. ReAct agents couldn’t reliably decide when to use which—leading to failures in hybrid environments.
Why Graphs Are Perfect for Browser Agents
Graphs solve these problems by embracing one key idea: break complex tasks into simple, connected steps.
1. Task Decomposition = Reliability
Each graph node handles a small, focused job—like “click search” or “fill out step 4 of the form” This simplifies context and improves reliability dramatically.
2. Full Observability
Graphs make the invisible visible. Every state transition is logged, every decision point is captured. When something goes wrong, we can pinpoint exactly where and why. Our users can see their automations running in real time and trust the process, especially when handling semi-deterministic workflows.
3. Deterministic Safety Guarantees
Here’s where graphs really shine for browser automation: conditional tool access. Different nodes can have access to different capabilities based on where they are in the workflow.
💡 Pro tip: You can require a specific DOM element (e.g., “Form submitted!”) before marking a task complete. Now we can detect it, transition to “Finish Node” and have Zero false positives.
4. Composability and Flexibility
Real-world browser automation isn’t just about AI—it’s about combining AI with deterministic code, different models for different tasks, and robust error handling. Graphs let us compose these elements naturally:
- Fast, lightweight models for simple navigation
- Powerful vision models for complex page understanding
- Deterministic scripts for running custom logic
- Specialized error recovery workflows
- Non-browser integrations (webhooks, MCPs, APIs)
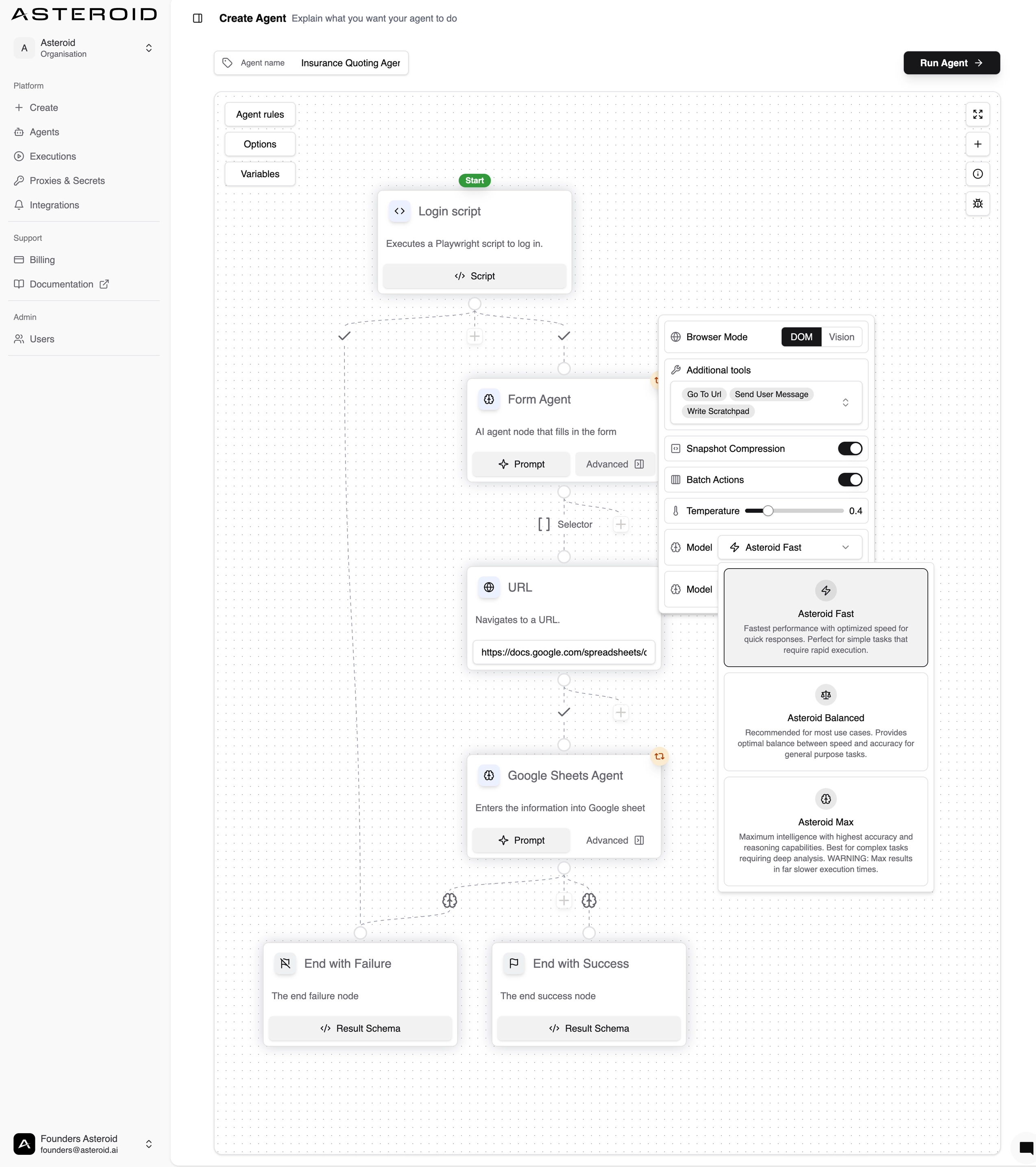
Building Graph-Based Browser Agents: The Architecture
🚀 Want to try it? Build your own agent in Asteroid.
:::arcade src=“https://app.arcade.software/share/ziD1VT2HimFZJHVFHJXU” :::
Our graph-based browser agents consist of nodes and edges, just like normal graphs:
Nodes: Focused modules that combine LLM reasoning with browser tool execution. Each node has a clear responsibility and constrained context.
Edges: Smart transitions between nodes that determine workflow progression based on execution results.
The magic happens in the transitions between nodes. For browser agents, we’ve identified two main methods for state transitions:
1. Agent-Driven Transitions
The current node’s agent decides when its task is complete and which node should execute next. Works well for complex decision points where AI reasoning is needed.
2. Deterministic Transitions
Code-based transitions triggered by specific conditions—page loads, element appearances, data validation results. These provide the strongest reliability guarantees.
The Path Forward
ReAct agents aren’t dead—they just aren’t ideal for workflows that demand control, reliability, and observability. For that, graphs are better.
We’re building Asteroid for non-technical teams too—giving them the tools to inspect, supervise, and edit automations themselves.
🧑🚀 The next step? Letting AI build and update the browser graph agents.
Ready to build a browser agent? Get started with Asteroid or book an onboarding demo.